Tuesday, 25 January 2022
BLACK FUNGUS ?
Monday, 24 January 2022
Covid 19 , RT PCR and CT value.
What is a COVID-19 PCR test?
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for COVID-19 is a molecular test that analyzes your upper respiratory specimen, looking for genetic material (ribonucleic acid or RNA) of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Scientists use the PCR technology to amplify small amounts of RNA from specimens into deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which is replicated until SARS-CoV-2 is detectable if present. The PCR test has been the gold standard test for diagnosing COVID-19 since authorized for use in February 2020. It’s accurate and reliable.
What is CT value in RT-PCR?
Every RT-PCR report underscores an important parameter Cycle Threshold, commonly known as CT value. The value determines whether the individual is COVID-positive or not.
What is the normal CT value in the RT-PCR report?
The Government of India has fixed the CT value at 35. If the CT value is below 35, the person is COVID positive and if above 35, the individual is COVID negative. Globally, the CT value ranges between 35-40 to determine the infection.

Wednesday, 25 March 2020
STATE OF FOREST REPORT 2019
STATE OF FOREST REPORT 2019
The report is published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) which has been mandated to assess the forest and tree resources of the country including wall-to-wall forest cover mapping in a biennial cycle. Starting 1987, 16 assessments have been completed so far. ISFR 2019 is the 16th report in the series.
SALIENT FEATURES
• India is among the few countries in the world where forest c over is consistently increasing.
• Total forest and tree cover of the country is 80.73 million hectare which is 24.56 percent of the geographical area.
ο Total forest cover – 21.67%
ο Tree cover – 2.89%
• As compared to 2017, there is an increase of 5188 sq km in t he total forest and total tree cover (forest cover – 3976 sq k m; tree cover – 1,212 sq km).
• Forest cover in the hill districts is 40.3%.
• Total forest cover in the tribal districts is 37.54%.
• Forest cover within the reserved forest are has shown a slight decrease of 330 sq km (0.05%).
• Highest range increase in forest cover has been observed i n open forest followed by very dense forest and moderately dense forest.
• Top three states showing increase in forest cover are Karnataka (1,025 sq. km) followed by Andhra Pradesh (990 sq km) and Kerala (823 sq km), Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh.
• Total Forest cover in the North Eastern Region is 65.05% of its geographical area. Current assessment shows a decrease of forest cover to the extent 0.45% in the region.
Except Assam and Tripura, all the States in the region show d ecrease in forest cover.
• Soil Organic Carbon represents the largest pool for carbon stock in forests – 56% to the total forest carbon stock of t he country
Area-wise Madhya Pradesh has the largest forest cover i n the country followed by Arunachal Pradesh, C hhattisgarh, Odisha and Maharashtra.
• In terms of forest cover as percentage of total
geographical area, the top five States are Mizoram
(85.41%), Arunachal Pradesh (79.63%), Meghalaya
(76.33%), Manipur (75.46%) and Nagaland (75.31%).
• Mangrove cover has been separately reported in the ISFR 2019
ο Total mangrove cover in the country is 4,975 sq km.
ο An increase of 54 sq Km in mangrove cover has been observed as compared to the previous assessment of
2017.
ο Top three states showing mangrove cover increase are Gujarat (37 sq km) followed by Maharashtra (16 sq km) and Odisha (8 sq km).
• The extent of bamboo bearing area of the country has been estimated 16.00 million hectare – an increase of 0.32 million hectare.
• Under the current assessment the total carbon stock in country’s forest is estimated 7,124.6 million tonnes and there an increase of 42.6 million tonnes in the carbon stock of country as compared to the last assessment of 2017.
• FSI has carried out an exercise at the national level to identify wetlands of more than 1 ha within RFA.
ο There are 62,466 wetlands covering 3.8% of the area
within the RFA/GW of the country.
ο Total number of wetlands located within reserved forest area is 8.13%.
ο Amongst the States, Gujarat has largest area of
wetlands within reserved forest area followed by West
Bengal.
• The report included a chapter on forest and people which collects information on the dependence of the people living in close proximity to forests for their day to day needs for forest produce such as Fuelwood, Fodder, Small timber and bamboo.
Follow click here

Monday, 23 March 2020
Asteroid Fast Facts ❤Aovious
What Are The Differences Between An Asteroid, Comet, Meteoroid, Meteor and Meteorite?
Source NASA TV FOLLOW ME CLICK HERE
Asteroid: A relatively small, inactive, rocky body orbiting the Sun.
Comet: A relatively small, at times active, object whose ices can vaporize in sunlight forming an atmosphere (coma) of dust and gas and, sometimes, a tail of dust and/or gas.
Meteoroid: A small particle from a comet or asteroid orbiting the Sun.
Meteor: The light phenomena which results when a meteoroid enters the Earth's atmosphere and vaporizes; a shooting star.
Meteorite: A meteoroid that survives its passage through the Earth's atmosphere and lands upon the Earth's surface.
Size and Frequency
Every day, Earth is bombarded with more than 100 tons of dust and sand-sized particles.
About once a year, an automobile-sized asteroid hits Earth's atmosphere, creates an impressive fireball, and burns up before reaching the surface.
Every 2,000 years or so, a meteoroid the size of a football field hits Earth and causes significant damage to the area.
Only once every few million years, an object large enough to threaten Earth's civilization comes along. Impact craters on Earth, the moon and other planetary bodies are evidence of these occurrences.
Space rocks smaller than about 25 meters (about 82 feet) will most likely burn up as they enter the Earth's atmosphere and cause little or no damage.
If a rocky meteoroid larger than 25 meters but smaller than one kilometer ( a little more than 1/2 mile) were to hit Earth, it would likely cause local damage to the impact area.
We believe anything larger than one to two kilometers (one kilometer is a little more than one-half mile) could have worldwide effects. At 5.4 kilometers in diameter, the largest known potentially hazardous asteroid is Toutatis.
By comparison, asteroids that populate the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, and pose no threat to Earth, can be as big as 940 kilometers (about 583 miles) across.
How is an Asteroid Orbit Calculated?
An asteroid's orbit is computed by finding the elliptical path about the sun that best fits the available observations of the object. That is, the object's computed path about the sun is adjusted until the predictions of where the asteroid should have appeared in the sky at several observed times match the positions where the object was actually observed to be at those same times. As more and more observations are used to further improve an object's orbit, we become more and more confident in our knowledge of where the object will be in the future.
What is NASA doing to find and learn more about potentially hazardous asteroids and comets?
NASA has established a Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO), managed in the Planetary Science Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.
The PDCO ensures the early detection of potentially hazardous objects (PHOs) - asteroids and comets whose orbits are predicted to bring them within 0.05 Astronomical Units of Earth (5 million miles or 8 million kilometers) and of a size large enough to reach Earth's surface - that is, greater than approximately 30 to 50 meters. NASA tracks and characterizes these objects and issues warnings about potential impacts, providing timely and accurate information. NASA also leads the coordination of U.S. Government planning for response to an actual impact threat.

Friday, 20 March 2020
INTERNET AS BASIC RIGHT
Why in news?
Recently, Supreme Court has delivered verdict on
a bunch of petitions challenging the restrictions
imposed on internet services and movement of
people in Jammu and Kashmir.
Provisions for Internet shutdowns in India
• Suspension of Internet services are dealt with
under the Information Technology Act, 2000,
the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC), 1973 and
the Telegraph Act, 1885. Supreme Court’s observation
• On Internet shutdown
through the medium of internet is a
fundamental right under Article 19(1)(a)
of the Constitution.
The restrictions on internet have to follow
the principles of proportionality under
Article 19(2).
✓ The doctrine essentially signifies that
the punishment should not be
disproportionate to the offence
committed or the nature and extent
of the State’s interference with the
exercise of a right must be
proportionate to the goal it seeks to
achieve.
Freedom of trade and commerce through
internet is also a constitutionally
protected right under Article 19(1)(g).
Suspension of internet for indefinite
period not permissible.
• On Section 144 of CrPC:
When Sec 144 is imposed for reasons of
apprehended danger, that danger must
be an “emergency”.
Powers under Sec 144 should be
exercised in a reasonable and bona fide
manner, and the order must state
material facts in order to enable judicial
review
Section 144 CrPC
• Powers under the law:
o It is a colonial era law that empowers a
district magistrate, a sub-divisional
magistrate or any other executive magistrate
empowered by the state government to issue
orders to prevent and address urgent cases of
apprehended danger or nuisance.
o This usually includes restrictions on
movement, carrying arms and from
assembling unlawfully. It is generally believed
that assembly of three or more people is
prohibited under Section 144. However, it can
be used to restrict even a single individual.
• Duration of the order: Order passed under Section
144 cannot remain in force for more than two
months from the date of the order, unless the
state government considers it necessary. Even
then, the total period cannot extend to more than
six months.
Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public
Emergency or Public Service) Rules, 2017 (Suspension
Rules)
• These Rules were framed by Ministry of
Communications under the Indian Telegraph Act,
which talks about interception of messages in the
“interests of the sovereignty and integrity of
India”.
• It empowers the government to block
transmission of messages in case of a public
emergency or for public safety in any part of the
country.
• Any order suspending internet under the Rules,
can be only for a temporary duration and not for
an indefinite period.
Other judgements on Internet as right
• In Faheema Shirin v. State of Kerala, the Kerala
High Court declared the right to Internet access as
a fundamental right, forming part of right to
privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution of
India.
Follow me click here

Sunday, 8 March 2020
Día Internacional de la Mujer | International Women’s Day
International Women’s Day is annually held on March 8 to celebrate women’s achievements throughout history and across nations. It is also known as the United Nations (UN) Day for Women’s Rights and International Peace.
Background
What Do People Do?
Public Life
- Azerbaijan.
- Armenia.
- Belarus.
- Kazakhstan.
- Moldova
- Russia.
- Ukraine.
Symbols
External Links

Wednesday, 26 February 2020
TROPICAL AND TEMPERATE CYCLONE
Tropical Cyclone | Temperate Cyclone | |
Origin | Thermal Origin | Dynamic Origin – Coriolis Force, Movement of air masses. |
Latitude | Confined to 100 – 300 N and S of equator. | Confined to 350 – 650 N and S of equator. More pronounced in Northern hemisphere due to greater temperature contrast. |
Frontal system | Absent | The very cyclone formation is due to frontogenesis.[Occluded Front] |
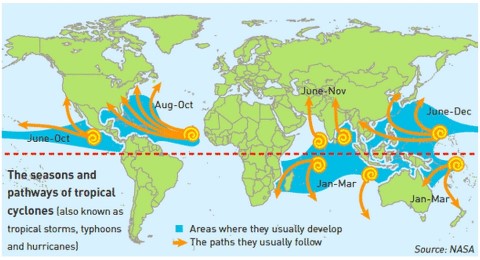
Formation | They form only on seas with temperature more than 26-270 C. They dissipate on reaching the land. | Can form both on land as well as seas |
Season | Seasonal: Late summers (Aug – Oct) | Irregular. But few in summers and more in winters. |
Size | Limited to small area.
Typical size: 100 – 500 kms in diameter.
Varies with the strength of the cyclone.
| They cover a larger area.
Typical size: 300 – 2000 kms in diameter. Varies from region to region.
|
Shape | Elliptical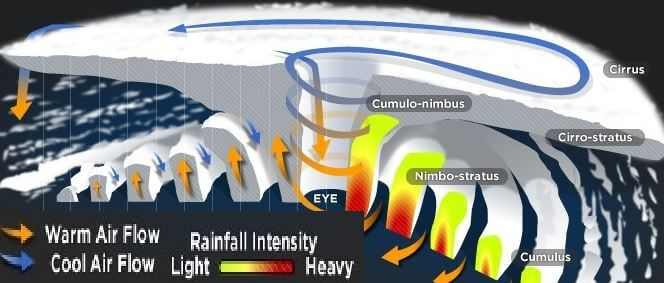 | Inverted ‘V’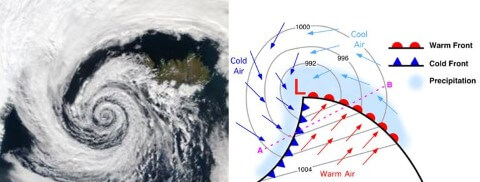 |
Rainfall | Heavy but does not last beyond a few hours. If the cyclone stays at a place, the rainfall may continue for many days. | In a temperate cyclone, rainfall is slow and continues for many days, sometimes even weeks. |
Wind Velocity and destruction | Much greater (100 – 250 kmph)(200 – 1200 kmph in upper troposphere)
Greater destruction due to winds, storm surges and torrential rains.
| Comparatively low. Typical range: 30 – 150 kmph.
Less destruction due to winds but more destruction due to flooding.
|
Isobars | Complete circles and the pressure gradient is steep | Isobars are usually ‘V’ shaped and the pressure gradient is low. |
Life time | Doesn’t last for more than a week | Last for 2-3 weeks. |
Path | East – West. Turn North at 200 latitude and west at 300 latitude.
Move away from equator.
The movement of Cyclones in Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal is a little different.
Here, these storms are superimposed upon the monsoon circulation of the summer months, and they move in northerly direction along with the monsoon currents.
 | West – East (Westerlies – Jet Streams). Move away from equator.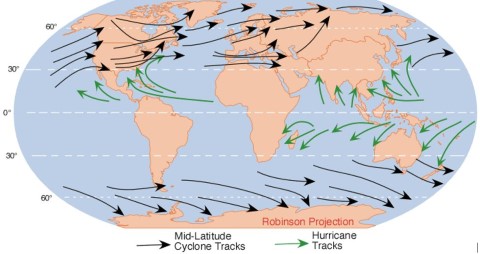 |
Temperature distribution | The temperature at the center is almost equally distributed. | All the sectors of the cyclone have different temperatures |
Calm region | The center of a tropical cyclone is known as the eye. The wind is calm at the center with no rainfall. | In a temperate cyclone, there is not a single place where winds and rains are inactive. |
Driving force | The tropical cyclone derives its energy from the latent heat of condensation, and the difference in densities of the air masses does not contribute to the energy of the cyclone. | The energy of a temperate cyclone depends on the densities of air masses. |
Influence of Jet streams | The relationship between tropical cyclones and the upper level air-flow is not very clear. | The temperate cyclones, in contrast, have a distinct relationship with upper level air flow (jet streams, Rossby waves etc.)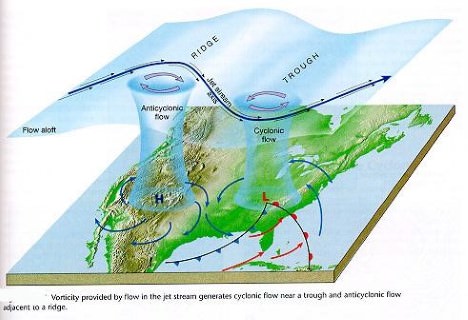 |
Clouds | The tropical cyclones exhibit fewer varieties of clouds – cumulonimbus, nimbostratus, etc.. | The temperate cyclones show a variety of cloud development at various elevations.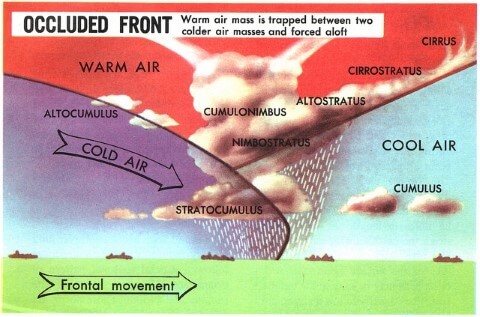 |
Surface anti-cyclones | The tropical cyclones are not associated with surface anticyclones and they have a greater destructive capacity. | The temperate cyclones are associated with anticyclones which precede and succeed a cyclone. These cyclones are not very destructive. |
Influence on India | Both coasts effected. But east coast is the hot spot. | Bring rains to North – West India. The associated instability is called ‘Western Disturbances’. |
- Titbit: In certain instances, two cyclones move toward each other and revolve around one another, with the smaller and less intense one moving more quickly. This phenomenon is called the Fujlwara effect.
Follow me click here 
Wednesday, 19 June 2019
Tricks to remember Important National and International days and dates
List of Important National and International days and dates
Https://www.facebook.com/Aovious1

BLACK FUNGUS ?
Explained: What is mucormycosis or ‘black fungus’ in Covid-19 patients, its symptoms and treatment Mucormycosis, a serious fungal infecti...

-
Climate has been defined as the average weather conditions at a specific place over a lengthy period of time, i.e., more than 30 years, wh...
-
© http://www.facebook.com/Aovious1 In news: NITI Ayog came with a national strategy to fight maternal and child malnutrition and anae...






